what are the nominal rfid tags mhz RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions. NFC Reader is a simple and efficient tool letting you to read contact-less tags on your smartphones and tablets. NFC Reader supports various tags like NDEF, RFID, FeliCa, ISO 14443, Mifare Classic 1k, MIFARE .
0 · rfid tags frequency
1 · rfid tags explained
2 · rfid tag read range chart
3 · rfid high frequency range
4 · rfid frequency chart
5 · low frequency rfid tags
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · hid rfid tag range
Retrofit NFC - Option 1 You have a total of three options for retrofitting NFC on your .
RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.The ultra high frequency range includes frequencies from 300 to 1000 MHz, but only two .RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.The ultra high frequency range includes frequencies from 300 to 1000 MHz, but only two frequency ranges, 433 MHz and 860–960 MHz, are used for RFID applications. The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags.
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications. #1. What Is Read Range? Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader. #2. How Is Read Range Determined? Generally, the manufacturer spec sheet includes RFID read range information.
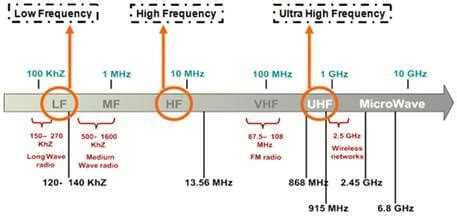
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.High-frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 MHz, and are easily distinguishable by their coiled antenna. HF tags typically have a thicker copper antenna that doesn’t loop as many times as the LF tag’s antenna (see image below).Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio waves to uniquely identify tagged objects. RFID Technology operates in four main frequency bands. Low Frequency (LF): 125 and 135 KHz. High Frequency (HF): 13.56 MHz (1.75 MHz to 13.56 MHz) Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): 860-960 MHz (Vary based on Region / Country - See table below)
The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags whereas the 860-960 MHz frequency range is used mostly for passive tags as well as some semi-passive tags. The 860-960 MHz frequency range is generally termed as one frequency, either 900 MHz or 915 MHz.The operating frequency of high frequency RFID tags (mainly 13.56 MHz) generally ranges from 3 MHz to 30 MHz. The global uniform frequency of the HF tag makes it suitable for a variety of RFID applications, especially in scenarios that require medium-range reading. Power supply, read range, and multi-tag capability.RFID tag range refers to the maximum distance at which an RFID reader can effectively read the tag’s information. This range is influenced by several factors, including the type of tag, the power of the reader, and environmental conditions.The ultra high frequency range includes frequencies from 300 to 1000 MHz, but only two frequency ranges, 433 MHz and 860–960 MHz, are used for RFID applications. The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags, while the 860–960 MHz range is used mostly for passive tags and some semi-passive tags.
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
rfid tags frequency

rfid tags explained
#1. What Is Read Range? Read range is the distance from which an RFID tag can be detected. The read range expresses the distance from which the tag receives just enough power to be activated to send back a signal to the reader. #2. How Is Read Range Determined? Generally, the manufacturer spec sheet includes RFID read range information. RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.

High-frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 MHz, and are easily distinguishable by their coiled antenna. HF tags typically have a thicker copper antenna that doesn’t loop as many times as the LF tag’s antenna (see image below).
Passive RFID tags harness energy from an RFID reader’s emitted Radio-frequency (RF) signal. When the reader sends a signal, it creates an electromagnetic field that energizes the tag. The tag captures this energy and powers its internal chip, enabling it to transmit data back to the reader. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio waves to uniquely identify tagged objects. RFID Technology operates in four main frequency bands. Low Frequency (LF): 125 and 135 KHz. High Frequency (HF): 13.56 MHz (1.75 MHz to 13.56 MHz) Ultra-High Frequency (UHF): 860-960 MHz (Vary based on Region / Country - See table below)The 433 MHz frequency is used for active tags whereas the 860-960 MHz frequency range is used mostly for passive tags as well as some semi-passive tags. The 860-960 MHz frequency range is generally termed as one frequency, either 900 MHz or 915 MHz.

rfid tag read range chart
vistaprint nfc card
So, have Wired/Bluetooth switch pro controller connected to pc, use its nfc reader/writer to .
what are the nominal rfid tags mhz|high frequency rfid tags