smart card communication protocol A smart card may have the following generic characteristics:• Dimensions similar to those of a credit card. ID-1 of the See more $16.99
0 · The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals
1 · Smart card application protocol data unit
2 · Smart card
3 · Introduction to Smart Card Development on the Desktop
You will be responsible for paying for your own shipping costs for returning your item. Shipping costs are non-refundable. If you receive a refund, the cost of return shipping will be deducted from your refund. Any customs duty if any are paid by the importer. . See more
Contactless smart cards communicate with readers under protocols defined in the ISO/IEC 14443 standard. They support data rates of 106–848 kbit/s. These cards require only proximity to an antenna to communicate. Like smart cards with contacts, contactless cards do not have an internal power source. See more
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart . See more
A smart card may have the following generic characteristics:• Dimensions similar to those of a credit card. ID-1 of the See moreSmart cards have been advertised as suitable for personal identification tasks, because they are engineered to be tamper resistant. The chip usually implements some cryptographic algorithm. There are, however, several methods for recovering some of the . See moreThe first main advantage of smart cards is their flexibility. Smart cards have multiple functions which simultaneously can be an ID, a credit card, a stored-value cash card, and a repository of . See moreThe basis for the smart card is the silicon integrated circuit (IC) chip. It was invented by Robert Noyce at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1959. The invention of the silicon integrated . See more
The DS8007 and Smart Card Interface Fundamentals
FinancialSmart cards serve as credit or ATM cards, fuel cards, mobile phone SIMs, authorization cards . See more
The benefits of smart cards are directly related to the volume of information and applications that are programmed for use on a card. A single contact/contactless smart card can be programmed with multiple banking credentials, medical entitlement, driver's . See more In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the .
The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports .Star 40. master. README. Introduction to Smart Card Development on the Desktop. Table of .
Smart card application protocol data unit
Contactless smart cards communicate with readers under protocols defined in the ISO/IEC 14443 standard. They support data rates of 106–848 kbit/s. These cards require only proximity to an antenna to communicate. Like smart cards with contacts, contactless cards do not have an internal power source.
In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4 Organization, security and commands for interchange. [1] The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports all ISO 7816, EMV™, and GSM11-11 requirements. This one mixed-signal peripheral manages all the details of the interface between a microcontroller and two, independent smart cards.Star 40. master. README. Introduction to Smart Card Development on the Desktop. Table of Contents: Introduction. Requirements. Resources. Definitions. General Development. Smartcard Commands. Smartcard Responses. Answer to Reset (ATR) Development Envrionments. Windows. Linux. Java. Program - Example 1. Program - Example 2. Packaging in Java 9+.The following sections in this article describe how Windows uses the smart card architecture to select the correct smart card reader software, provider, and credentials for a successful smart card sign-in:
Smart card
ISO/IEC 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, and more recently, contactless mobile devices, managed jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).Discover the essentials of smart card technology with our comprehensive guide. Learn about the different types of smart cards, how they work, their applications, security features, and future trends. Explore how smart cards are used in banking, medical, telecommunications, and more, and get insights into the latest advancements and industry .
Communication with Smart Cards (Pages: 201-242) Summary. PDF. CHAPTER 9.In the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, which specifies organization, security, and commands for .
When logical channels are used, upto 19 applications in a single card can exchange data directly with the terminal. The chapter describes main features some protocols that includes TCP/IP protocol, HTTP protocol and Bearer Independent Protocol (BIP) and connecting terminals to higher-level systems.
Contactless smart cards communicate with readers under protocols defined in the ISO/IEC 14443 standard. They support data rates of 106–848 kbit/s. These cards require only proximity to an antenna to communicate. Like smart cards with contacts, contactless cards do not have an internal power source.In the context of smart cards, an application protocol data unit (APDU) is the communication unit between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4 Organization, security and commands for interchange. [1] The DS8007 is a multiprotocol, low-cost, dual, smart card interface that supports all ISO 7816, EMV™, and GSM11-11 requirements. This one mixed-signal peripheral manages all the details of the interface between a microcontroller and two, independent smart cards.Star 40. master. README. Introduction to Smart Card Development on the Desktop. Table of Contents: Introduction. Requirements. Resources. Definitions. General Development. Smartcard Commands. Smartcard Responses. Answer to Reset (ATR) Development Envrionments. Windows. Linux. Java. Program - Example 1. Program - Example 2. Packaging in Java 9+.

The following sections in this article describe how Windows uses the smart card architecture to select the correct smart card reader software, provider, and credentials for a successful smart card sign-in:ISO/IEC 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, and more recently, contactless mobile devices, managed jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).Discover the essentials of smart card technology with our comprehensive guide. Learn about the different types of smart cards, how they work, their applications, security features, and future trends. Explore how smart cards are used in banking, medical, telecommunications, and more, and get insights into the latest advancements and industry . Communication with Smart Cards (Pages: 201-242) Summary. PDF. CHAPTER 9.
Introduction to Smart Card Development on the Desktop
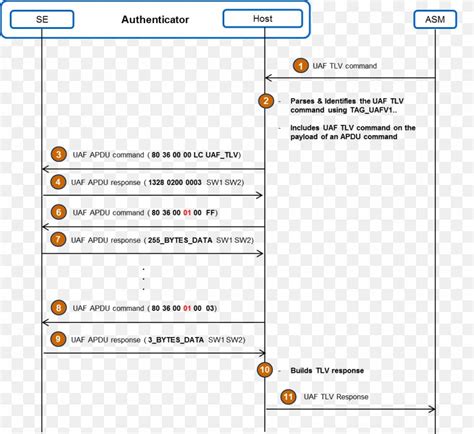
In the context of smart cards, an Application Protocol Data Unit (APDU) is the unit of communication between a smart card reader and a smart card. The structure of the APDU is defined by ISO/IEC 7816-4, which specifies organization, security, and commands for .
NFC tags are passive, meaning they don't have any power source. Instead, they literally draw power from the device that reads them, thanks to magnetic induction. When a reader gets close enough to a tag, it energizes it and .
smart card communication protocol|Smart card application protocol data unit