high frequency rfid card Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications. We only replace items if they are defective or damaged. If you need to exchange it for the same item, send us an email at
[email protected] . See more
0 · what frequency does rfid use
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · ultra high frequency rfid reader
3 · rfid frequency chart
4 · low frequency rfid tags
5 · highfid radio frequency tags
6 · high frequency rfid tags
7 · disposable high frequency rfid tags
A quote from the docs. Android 4.4 and higher provide an additional method of card emulation .
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
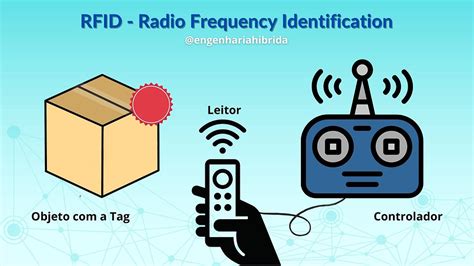
Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware.
1. Low Frequency (LF) RFID. Characteristics: Frequency Range: 125 kHz or 134 kHz. Read Range: 10 cm to 1 meter (4 inches to 3 feet) Data Transfer Rate: Slow. Sensitivity to Interference: Less sensitive to interference from liquids and metals. Cost: Typically, higher than UHF systems. Applications:
High-Frequency (HF) RFID Cards. The operating frequency of high-frequency RFID cards is 13.56 MHz, and they are mainly used in payment systems, library management, public transportation, and other fields. High-frequency cards offer fast data .
Discover the factors that impact the RFID tag range and how to choose the right tag for your needs. Learn about different tag types, frequencies, and ways to optimize RFID performance.The high frequency range includes frequencies from 3 to 30 MHz but only one frequency, 13.56 MHz, is used for RFID applications. This frequency is now available for RFID applications worldwide with the same power level. Tags and interrogators using 13.56 MHz are generally called the HF tags and the HF interrogators. High-Frequency tags. High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and .The high frequency (HF) band on the RF spectrum extends from 3 MHz to 30 MHz. The wavelength of a high frequency wave is much shorter than an LF wave – only around 22 meters, or a little less than 2 school buses in length.
The RFID cards use different frequency bands, including 125 kHz Low Frequency (LF), 13.56 MHz High Frequency (HF), and 860-960 Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). The frequency band of each card will determine its applications.High-Frequency RFID (HF) High-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 3 MHz and 30 MHz. This range offers longer reading distances, typically up to 1 meter. HF RFID is commonly used in applications such as library management, public transportation payment systems, and inventory tracking.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
Low Frequency RFID & High Frequency RFID have 8 key differences that set them apart - the actual frequency range , data rates, write capabilities, environmental concerns, read range, tag formats, RFID applications, RFID hardware. 1. Low Frequency (LF) RFID. Characteristics: Frequency Range: 125 kHz or 134 kHz. Read Range: 10 cm to 1 meter (4 inches to 3 feet) Data Transfer Rate: Slow. Sensitivity to Interference: Less sensitive to interference from liquids and metals. Cost: Typically, higher than UHF systems. Applications:High-Frequency (HF) RFID Cards. The operating frequency of high-frequency RFID cards is 13.56 MHz, and they are mainly used in payment systems, library management, public transportation, and other fields. High-frequency cards offer fast data .Discover the factors that impact the RFID tag range and how to choose the right tag for your needs. Learn about different tag types, frequencies, and ways to optimize RFID performance.
The high frequency range includes frequencies from 3 to 30 MHz but only one frequency, 13.56 MHz, is used for RFID applications. This frequency is now available for RFID applications worldwide with the same power level. Tags and interrogators using 13.56 MHz are generally called the HF tags and the HF interrogators.
windows 10 disable smart card login
High-Frequency tags. High Frequency (HF) tags operate at 13.56 megahertz. They are essentially the ‘Swiss army knife of the RFID world. They have data transfer rates acceptable for many uses, a wide range of storing capacities and .
The high frequency (HF) band on the RF spectrum extends from 3 MHz to 30 MHz. The wavelength of a high frequency wave is much shorter than an LF wave – only around 22 meters, or a little less than 2 school buses in length. The RFID cards use different frequency bands, including 125 kHz Low Frequency (LF), 13.56 MHz High Frequency (HF), and 860-960 Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). The frequency band of each card will determine its applications.
what frequency does rfid use
ultra high frequency rfid tags
ultra high frequency rfid reader
Even if your debit or credit card does not have a contactless indicator, it doesn’t matter. Through your Token Smart Ring, you can make touch-free purchases at any merchants that support contactless payments. But of course, you need to register your Visa- or MasterCard-branded debit and credit cards first through the Token app.
high frequency rfid card|high frequency rfid tags